7 Most VSAQ’s of Locomotion and Reproduction Chapter in Inter 1st Year Zoology (TS/AP)
2 Marks
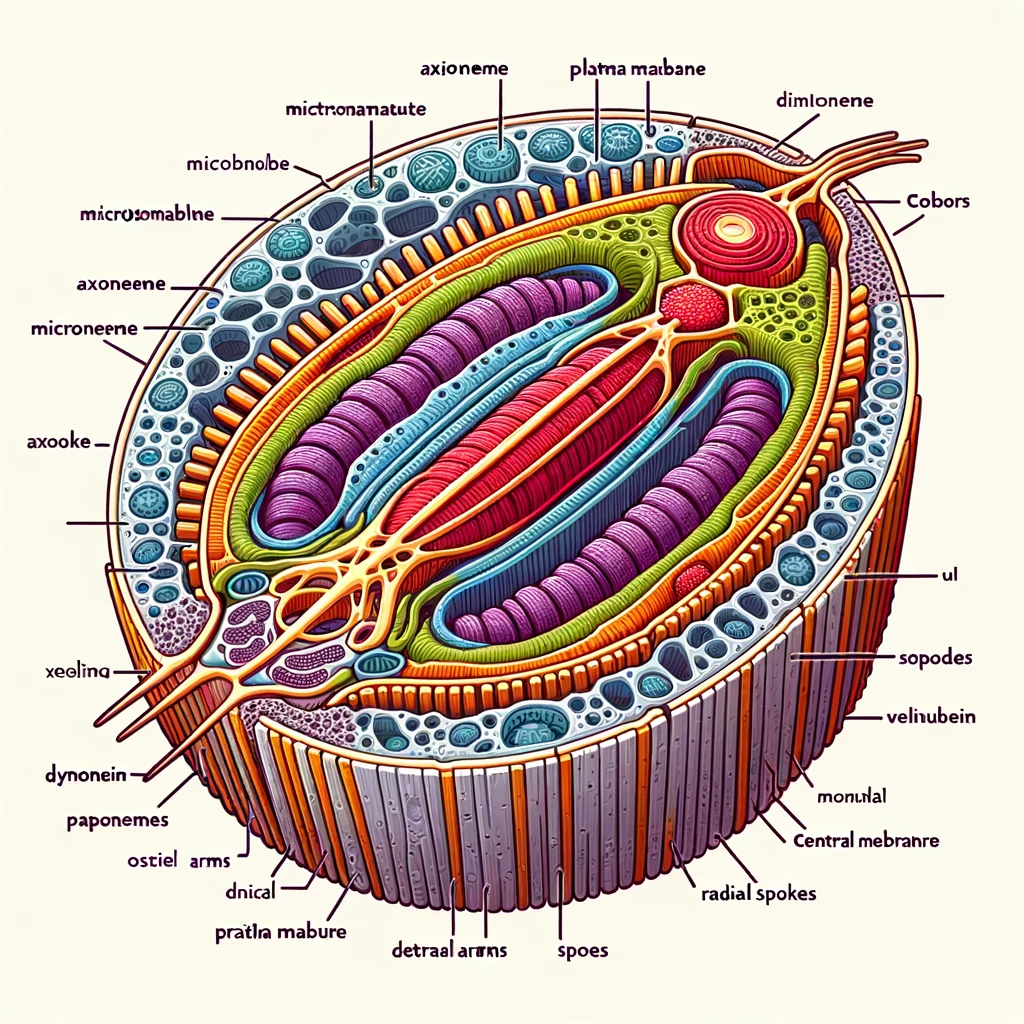
VSAQ-1 : Draw a labelled diagram of T.S of flagellum.
VSAQ-2 : List any two differences between a flagellum and cilium.
- Flagellum: Long, whip-like, undular movement, primarily for locomotion.
- Cilium: Small, hair-like, pendular movement, used for locomotion, food collection, material movement, and sensory functions.
VSAQ-3 : What is a kinety?
- A kinety is a row of kinetosomes (granules) and kinetodesmata (fibers) found longitudinally in ciliates.
- It is a component of the infra-ciliary system, contributing to the ciliate’s locomotion and movement.
VSAQ-4 : Distinguish between synchronous and metachronous movements.
Synchronous Movements:
- In synchronous movement, cilia in a transverse row beat simultaneously in one direction.
- This results in a coordinated, unidirectional motion of the cilia.
Metachronous Movements:
- In metachronous movement, cilia in a longitudinal row beat sequentially, one after another.
- This creates a wave-like pattern, resembling the motion of wind passing over a paddy field.
VSAQ-5 : Distinguish between Proter and opisthe.
Proter:
- The proter is the anterior individual in a ciliate conjugation.
- It receives the anterior contractile vacuole, cytopharynx, and cytostome from the parent during conjugation.
Opisthe:
- The opisthe is the posterior individual in a ciliate conjugation.
- It receives the posterior contractile vacuoles and develops other organelles during the conjugation process.
VSAQ-6 : Distinguish between lobopodium and filopodium.
Lobopodium:
- Lobopodium is a type of pseudopodium characterized by its blunt, finger-like appearance.
- It is commonly found in organisms like Amoeba and Entamoeba.
Filopodium:
- Filopodium is a type of pseudopodium characterized by its long, fiber-like structure.
- It is typically found in organisms like Euglypha.
VSAQ-7 : Define conjugation with reference to ciliates. Give two examples.
Conjugation is a temporary union between two mature ciliates belonging to different mating types. During this process, they exchange nuclear material to enhance genetic diversity and rejuvenate their vitality. Two examples of ciliates that undergo conjugation are Paramecium caudatum and Tetrahymena thermophila.
