Human Reproductive System (VSAQs)
Zoology-2 | Unit-5A: Human Reproductive System – VSAQs:
Welcome to VSAQs in Unit-5A: Human Reproductive System. This page includes the most important FAQs from previous exams. Each answer is presented in the exam format to help you prepare effectively and aim for top marks in your final exams.
VSAQ-1: Where Are the Testes Located in Man? Name the Protective Coverings of Each Testis.
In men, the testes are housed in a special pouch called the scrotum, which hangs outside the abdomen. This location is crucial because it keeps the testes at a temperature slightly cooler than the rest of the body, which is necessary for sperm production. Each testis is carefully protected by a tough, fibrous layer known as the tunica albuginea. Additionally, there’s an outer layer called the tunica vaginalis, which acts as a second shield, keeping the testes safe and ensuring they function properly in producing sperm and male hormones, vital for reproductive health.
VSAQ-2: What Are the Functions of Sertoli Cells of the Seminiferous Tubules and the Leydig Cells in Man?
Inside the testes, Sertoli cells play a crucial role. Imagine them as caretakers within the seminiferous tubules—the place where sperm is produced. These cells provide both physical support and nourishment to developing sperm, ensuring they grow strong and healthy. They also produce a hormone called inhibin, which helps regulate the production of sperm by controlling the levels of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) in the body.
Meanwhile, Leydig cells, located in the spaces between the seminiferous tubules, are like hormone factories. Their main job is to produce testosterone, the hormone responsible for developing male secondary sexual characteristics like muscle growth, a deeper voice, and facial hair. Testosterone also plays a vital role in maintaining reproductive health, making these cells essential to the male reproductive system.
VSAQ-3: Name the Yellow Mass of Cells Accumulated in the Empty Follicle After Ovulation. Name the Hormone Secreted by It and What Is Its Function?
After ovulation, when the egg is released from the follicle, the empty follicle transforms into a yellow mass of cells known as the corpus luteum. This structure plays a key role in the menstrual cycle by secreting the hormone progesterone. Progesterone helps thicken and maintain the uterine lining, making it ready for the possible implantation of a fertilized egg. If fertilization occurs, the corpus luteum continues to produce progesterone, supporting the early stages of pregnancy until the placenta takes over. However, if fertilization doesn’t happen, the corpus luteum eventually breaks down, leading to a drop in progesterone levels, which triggers menstruation.
VSAQ-4: Define Gestation Period. What Is the Duration of Gestation Period in Human Beings?
The gestation period is the time during which a baby develops inside the mother’s uterus, starting from fertilization and ending with childbirth. In humans, this period typically lasts about 38 weeks from fertilization, or around 40 weeks if counted from the start of the last menstrual cycle. During this time, the embryo undergoes various stages of development, gradually growing and maturing until it’s ready for birth.
VSAQ-5: What Is Implantation, With Reference to Embryo?
Implantation is a critical step in early pregnancy, occurring about 6 days after fertilization. This is when the embryo attaches itself to the uterine wall, specifically the endometrial lining. This connection is essential because it allows the embryo to receive nutrients and oxygen from the mother’s bloodstream, which are vital for its development. Once implantation is successful, the embryo continues to grow within the uterus, eventually developing into a baby ready for birth.
VSAQ-6: What Is the Menstrual Cycle? Which Hormones Regulate the Menstrual Cycle?
The menstrual cycle is a natural process in the female reproductive system, preparing the body for potential pregnancy each month. Think of it as a monthly routine where an egg, or ovum, is released from the ovaries, and the lining of the uterus thickens to create a cozy environment for a fertilized egg. If fertilization doesn’t occur, this lining is shed, resulting in menstruation, or what we commonly call a period. This cycle is regulated by a team of hormones—FSH (Follicle Stimulating Hormone), LH (Luteinizing Hormone), estrogen, and progesterone. Each plays a role in orchestrating the various phases of the cycle, ensuring everything happens smoothly. The entire cycle typically lasts around 28-29 days, although it can vary from one person to another.
VSAQ-7: Define Spermiogenesis and Spermiation.
Spermiogenesis is a fascinating process where immature sperm cells, known as spermatids, transform into mature, fully functional sperm cells, or spermatozoa. Imagine a caterpillar turning into a butterfly; similarly, these spermatids undergo significant changes, like developing a tail to swim and shedding unnecessary parts, to become the sleek, efficient cells ready for fertilization.
On the other hand, spermiation is the moment when these fully developed sperm cells are released from the testes. It’s like the sperm cells being set free, ready to embark on their journey through the male reproductive system and, eventually, during sexual activity, into the female reproductive tract, where they might meet an egg for fertilization.
VSAQ-8: What Is Parturition? Which Hormones Are Involved in Inducing Parturition?
Parturition is the scientific term for the process of giving birth. It’s the incredible journey where the baby leaves the mother’s uterus and enters the outside world. This process is driven by a powerful hormone called oxytocin, which plays a starring role in inducing labor. Oxytocin stimulates the uterus to contract, helping the baby move down the birth canal and facilitating a smooth delivery. It’s like the body’s natural way of signaling that it’s time for the baby to be born.
VSAQ-9: What Is Capacitation of Sperms?
Capacitation is a crucial process that takes place within the female reproductive tract, particularly in the uterus and fallopian tubes. Think of it as the sperm’s final preparation before the big event—fertilization. When sperm enter the female body, they aren’t immediately ready to fertilize an egg. They need to undergo certain physiological changes, which we call capacitation.
During this process, sperm experience alterations in their membrane and chemical composition, making them more agile and capable of successfully reaching and penetrating the egg. It’s like a runner stretching and warming up before a race. Capacitation ensures that sperm are fully “activated” and ready to fertilize the egg, which is a critical step in the initiation of pregnancy.
VSAQ-10: What Is Compaction in Human Development?
Compaction is a key event in the early stages of human development, particularly during the formation of the embryo. This process occurs at the morula stage, which is when the embryo resembles a solid ball of cells after several rounds of cell division.
During compaction, the individual cells within this ball, known as blastomeres, change their shape and start sticking closely together, almost like a team huddling up tightly. This tight binding creates a more compact and cohesive structure, which we call the compact morula. Compaction is important because it helps the cells communicate better with each other and establishes a structure needed for the next stages of development, including the formation of the blastocyst and successful implantation in the uterus. This process lays the groundwork for the embryo’s continued growth and development, eventually leading to the formation of a healthy baby. communication and establishing cell polarity. These processes are fundamental for subsequent developmental stages, including blastocyst formation and successful implantation in the uterus.
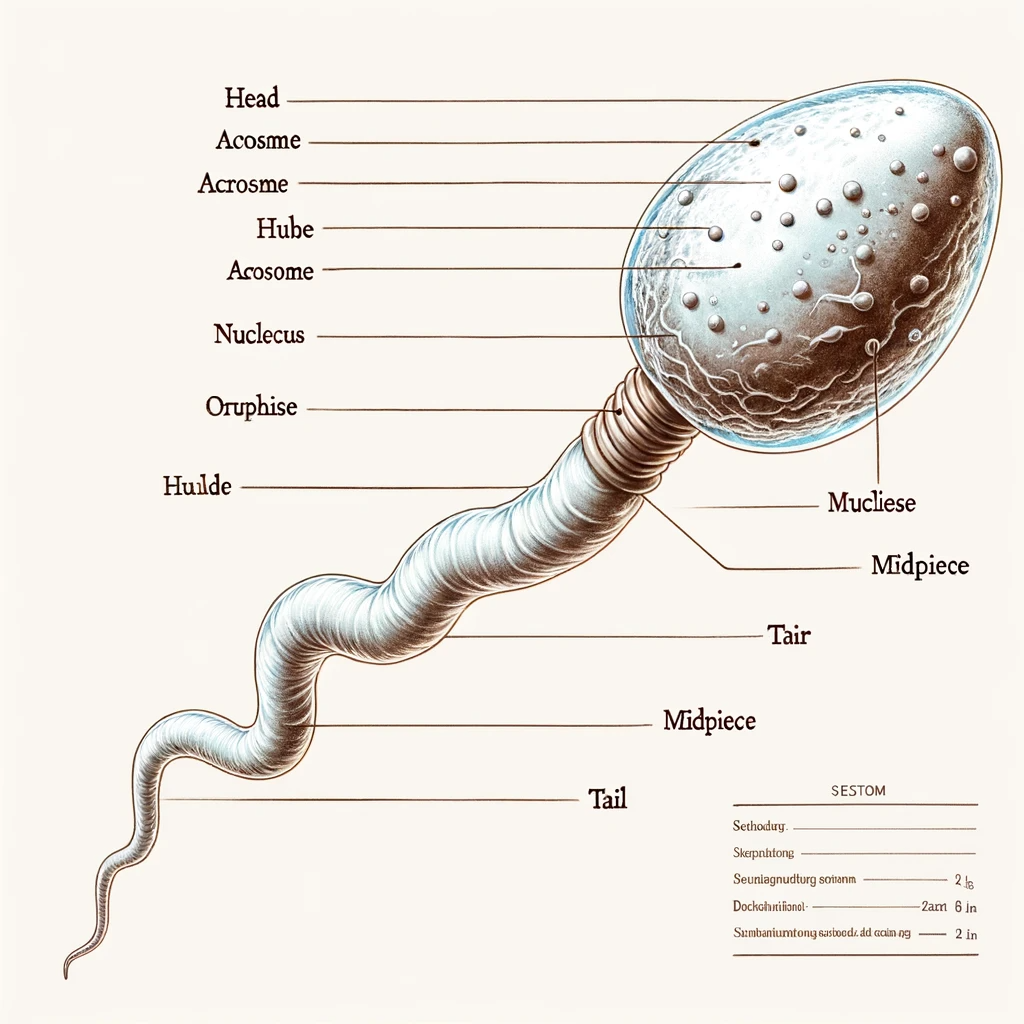
VSAQ-11 : Draw a labelled diagram of a Sperm.