Locomotion and Reproduction (SAQs)
Zoology-1 | 5. Locomotion And Reproduction – SAQs:
Welcome to SAQs in Chapter 5: Locomotion And Reproduction. This page includes the most important FAQs from previous exams. Each answer is provided in simple English, followed by a Telugu explanation, and then presented in the exam format. This method ensures you’re well-prepared to secure top marks in your final exams.
SAQ-1 : Describe the process of transverse binary fission in Paramecium.
For Backbenchers 😎
Special Way to Multiply: Paramecium is a tiny water creature, and when things are just right, they have a special way to make more of themselves, like making copies.
Getting Ready: Before they start making copies, Paramecium stops eating, like taking a break from meals. They also have a groove they use to eat, and it goes away for a bit.
Splitting in Two: Inside Paramecium, there are tiny parts that control things. These parts split into two: one in the front and one in the back. It’s like the brain dividing into two.
Cutting in Half: Now, imagine Paramecium as a tiny water balloon. In the middle, a part starts to pinch or squeeze. It shows where Paramecium is going to split into two new ones.
Making New Cells: As the pinch gets deeper, Paramecium breaks into two new cells. One becomes the front part, and the other becomes the back part.
Sharing Important Things: Each new cell gets important things from the parent, like a vacuum to clean waste and new control parts because the old ones split.
Growing What’s Missing: If anything important was left behind during the split, the new cells make it again, like fixing something that was missing.
Super Fast and Efficient: This whole process happens really, really quickly. In just about two hours, Paramecium can make new cells. And in just one day, they can make four generations of new cells! It’s like they’re super speedy at making more of themselves when everything is just right.
In a Nutshell: So, Paramecium has a speedy way to make copies of itself. They pause eating, divide into two parts, pinch in the middle, and become two new cells. Each new cell gets important stuff from the parent and grows what’s missing. They’re like tiny experts at multiplying when conditions are perfect!
మన తెలుగులో
గుణించడం కోసం ప్రత్యేక మార్గం: పారామీషియం ఒక చిన్న నీటి జీవి, మరియు విషయాలు సరిగ్గా ఉన్నప్పుడు, కాపీలు చేయడం వంటి వాటి గురించి మరింత ఎక్కువ చేయడానికి వారికి ఒక ప్రత్యేక మార్గం ఉంటుంది.
సిద్ధమవుతున్నారు: వారు కాపీలు చేయడం ప్రారంభించే ముందు, పారామీషియం భోజనం నుండి విరామం తీసుకోవడం వంటి వాటిని తినడం మానేస్తుంది. వారు తినడానికి ఉపయోగించే గాడిని కూడా కలిగి ఉంటారు మరియు అది కొంచెం పోతుంది.
రెండుగా విభజించడం: పారామీషియం లోపల, వస్తువులను నియంత్రించే చిన్న భాగాలు ఉన్నాయి. ఈ భాగాలు రెండుగా విభజించబడ్డాయి: ఒకటి ముందు మరియు వెనుక. మెదడు రెండుగా విడిపోయినట్లే.
సగానికి కత్తిరించడం: ఇప్పుడు, పారామీషియంను ఒక చిన్న నీటి బెలూన్గా ఊహించుకోండి. మధ్యలో, ఒక భాగం చిటికెడు లేదా స్క్వీజ్ చేయడం ప్రారంభిస్తుంది. పారామీషియం ఎక్కడ రెండు కొత్తవిగా విడిపోతుందో ఇది చూపిస్తుంది.
కొత్త కణాలను తయారు చేయడం: చిటికెడు లోతుగా ఉన్నందున, పారామీషియం రెండు కొత్త కణాలుగా మారుతుంది. ఒకటి ముందు భాగం అవుతుంది, మరొకటి వెనుక భాగం అవుతుంది.
ముఖ్యమైన విషయాలను పంచుకోవడం: ప్రతి కొత్త సెల్ పేరెంట్ నుండి ముఖ్యమైన విషయాలను పొందుతుంది, పాతవి విడిపోయినందున వ్యర్థాలను మరియు కొత్త నియంత్రణ భాగాలను శుభ్రం చేయడానికి వాక్యూమ్ వంటివి.
తప్పిపోయిన వాటిని పెంచడం: విభజన సమయంలో ముఖ్యమైనది ఏదైనా మిగిలి ఉంటే, కొత్త కణాలు దానిని మళ్లీ తయారు చేస్తాయి, తప్పిపోయిన దాన్ని పరిష్కరించడం వంటివి.
సూపర్ ఫాస్ట్ మరియు ఎఫెక్టివ్: ఈ మొత్తం ప్రక్రియ నిజంగా చాలా త్వరగా జరుగుతుంది. కేవలం రెండు గంటల్లో, పారామీషియం కొత్త కణాలను తయారు చేయగలదు. మరియు కేవలం ఒక రోజులో, వారు నాలుగు తరాల కొత్త కణాలను తయారు చేయగలరు! ప్రతిదీ సరిగ్గా ఉన్నప్పుడు వారు తమను తాము ఎక్కువగా తయారు చేసుకోవడంలో చాలా వేగంగా ఉన్నట్లు అనిపిస్తుంది.
క్లుప్తంగా: కాబట్టి, పారామీషియం దానినే కాపీలు చేయడానికి వేగవంతమైన మార్గాన్ని కలిగి ఉంది. అవి తినడం పాజ్ చేసి, రెండు భాగాలుగా విభజించి, మధ్యలో చిటికెడు, మరియు రెండు కొత్త కణాలుగా మారుతాయి. ప్రతి కొత్త సెల్ పేరెంట్ నుండి ముఖ్యమైన అంశాలను పొందుతుంది మరియు తప్పిపోయిన వాటిని పెంచుతుంది. పరిస్థితులు పరిపూర్ణంగా ఉన్నప్పుడు గుణించడంలో వారు చిన్నపాటి నిపుణులలా ఉన్నారు!
Introduction
Transverse binary fission is a fundamental reproductive process observed in the unicellular organism Paramecium, particularly under favorable conditions. This process is essential for understanding their rapid multiplication and growth.
Process of Transverse Binary Fission in Paramecium
- Favorable Conditions: Paramecium undergoes transverse binary fission primarily when environmental conditions are conducive to growth and reproduction.
- Feeding Stops: Before binary fission begins, Paramecium ceases feeding, and the oral groove (used for food intake) temporarily disappears.
- Micro Nucleus Division: The micro nucleus divides through mitosis, resulting in two identical nuclei.
- Macro Nucleus Division: The macro nucleus undergoes division by amitosis, forming two parts.
- Transverse Constriction: A transverse constriction forms in the cell’s middle, indicating the site of cell division.
- Formation of Daughter Individuals: The constriction deepens, eventually splitting the parent Paramecium into two daughter individuals.
- Proter and Opisthe: The anterior (front) daughter cell is referred to as the proter, and the posterior (rear) daughter cell as the opisthe.
- Vacuoles Inheritance: Each daughter cell inherits one contractile vacuole from the parent, and a second one is formed in each daughter cell.
- Nuclei Inheritance: The opisthe receives the posterior contractile vacuoles along with the newly formed macro and micro nuclei.
- Development of Missing Organelles: Missing organelles in the daughter cells are newly formed during the fission process.
- Duration: The entire transverse binary fission process in Paramecium typically completes in about two hours.
- Rapid Reproduction: Paramecium can produce up to four generations of offspring in a single day, highlighting its rapid reproductive capability.
- Homothetogenic Fission: The type of transverse binary fission observed in Paramecium is classified as homothetogenic fission.
Summary
Transverse binary fission in Paramecium is a key reproductive process occurring under favorable conditions. It involves the cessation of feeding, division of micro and macro nuclei, formation of a transverse constriction, and the eventual separation into two daughter cells – proter and opisthe. Each daughter cell inherits and develops necessary organelles, allowing Paramecium to reproduce rapidly and efficiently.
SAQ-2 : Describe the process of longitudinal binary fission in Euglena.
For Backbenchers 😎
Euglena’s Special Way to Multiply: Euglena is a tiny single-celled creature that lives in water. When everything is just right, they do something special to make more of themselves, like making copies.
Good Times for Euglena: This happens when everything is great for Euglena, like when they have enough food and the weather is nice.
Taking a Break: Before they start making copies, some parts inside Euglena, like their eye spot, go away for a little while.
Splitting in Two: Inside Euglena, there are tiny parts that control things. These parts split into two: one in the front and one in the back. It’s like the brain dividing into two.
Creating a Line: Imagine Euglena like a little swimming cucumber. In the front, they make a long, narrow line.
Drawing the Line: This line gets longer and moves toward the back. It’s like drawing a line to cut Euglena into two pieces.
Whip-Like Tails: Euglena uses whip-like tails called flagella to swim. After they split, one new Euglena keeps its old tails, and the other gets new ones.
Two Twins: At the end, Euglena becomes two identical cells. They’re like twin Euglena, and they can each grow and make more Euglena on their own. This is Euglena’s way of growing when everything is just right!
In Simple Words: So, Euglena is a tiny water creature that can make copies of itself when everything is perfect. Some parts take a break, they split into two cells, and each one can grow and make more Euglena. It’s like Euglena’s secret to growing when conditions are just right!
మన తెలుగులో
గుణించడం కోసం యూగ్లీనా యొక్క ప్రత్యేక మార్గం: యూగ్లీనా అనేది నీటిలో నివసించే ఒక చిన్న ఏకకణ జీవి. ప్రతిదీ సరిగ్గా ఉన్నప్పుడు, కాపీలు చేయడం వంటి తమ గురించి తాము ఎక్కువగా రూపొందించుకోవడానికి వారు ప్రత్యేకంగా ఏదైనా చేస్తారు.
యుగ్లీనాకు మంచి సమయం: యుగ్లీనాకు తగినంత ఆహారం ఉన్నప్పుడు మరియు వాతావరణం చక్కగా ఉన్నప్పుడు ఇది జరుగుతుంది.
విరామం తీసుకోవడం: వారు కాపీలు చేయడం ప్రారంభించే ముందు, యూగ్లీనాలోని కొన్ని భాగాలు, వారి ఐ స్పాట్ వంటివి, కొద్దిసేపు దూరంగా ఉంటాయి.
రెండుగా విభజించడం: యూగ్లీనా లోపల, వస్తువులను నియంత్రించే చిన్న భాగాలు ఉన్నాయి. ఈ భాగాలు రెండుగా విభజించబడ్డాయి: ఒకటి ముందు మరియు వెనుక. మెదడు రెండుగా విడిపోయినట్లే.
ఒక పంక్తిని సృష్టించడం: యూగ్లెనాను కొద్దిగా ఈత కొట్టే దోసకాయలా ఊహించుకోండి. ముందు భాగంలో, వారు పొడవైన, ఇరుకైన గీతను తయారు చేస్తారు.
రేఖను గీయడం: ఈ రేఖ పొడవుగా ఉంటుంది మరియు వెనుక వైపుకు కదులుతుంది. యూగ్లీనాను రెండు ముక్కలుగా కోయడానికి గీత గీసినట్లుంది.
విప్-లైక్ టెయిల్స్: యూగ్లీనా ఈత కొట్టడానికి ఫ్లాగెల్లా అని పిలువబడే విప్ లాంటి తోకలను ఉపయోగిస్తుంది. అవి విడిపోయిన తర్వాత, ఒక కొత్త యూగ్లెనా దాని పాత తోకలను ఉంచుతుంది మరియు మరొకటి కొత్త వాటిని పొందుతుంది.
ఇద్దరు కవలలు: చివరలో, యూగ్లెనా రెండు ఒకేలా కణాలుగా మారుతుంది. వారు జంట యూగ్లెనా లాగా ఉన్నారు, మరియు వారు ప్రతి ఒక్కరు పెరుగుతాయి మరియు ఎక్కువ యూగ్లెనాను సొంతంగా తయారు చేసుకోవచ్చు. ప్రతిదీ సరిగ్గా ఉన్నప్పుడు యూగ్లీనా ఎదగడానికి ఇదే మార్గం!
సాధారణ పదాలలో: కాబట్టి, యూగ్లెనా ఒక చిన్న నీటి జీవి, ఇది ప్రతిదీ సరిగ్గా ఉన్నప్పుడు దానినే కాపీలు చేయగలదు. కొన్ని భాగాలు విరామం తీసుకుంటాయి, అవి రెండు కణాలుగా విడిపోతాయి మరియు ప్రతి ఒక్కటి పెరుగుతాయి మరియు మరింత యూగ్లీనాను తయారు చేయగలవు. పరిస్థితులు సరిగ్గా ఉన్నప్పుడు పెరగడం యూగ్లీనా రహస్యం లాంటిది!
Introduction
Euglena, a unicellular organism, replicates through longitudinal binary fission under favorable conditions. This mode of reproduction involves the division of cellular components, resulting in the formation of two genetically identical daughter cells.
Process of Longitudinal Binary Fission in Euglena
- Favorable Conditions: Euglena undergoes longitudinal binary fission during conditions conducive to growth and reproduction.
- Disappearance of Structures: During fission, certain structures like the stigma (eyespot), paraflagellar body, and contractile vacuoles temporarily disappear.
- Division of Cellular Components: The nucleus, basal granules, chromatophores (sites of photosynthesis), and cytoplasm divide, preparing for the formation of daughter cells.
- Formation of Longitudinal Groove: A longitudinal groove forms at the anterior (front) end of the Euglena.
- Groove Extension: The groove extends progressively towards the posterior (rear) end, effectively dividing the organism into two halves.
- Flagella in Daughter Cells: Post-division, one daughter cell retains the original flagella, while the other develops new flagella.
- Symmetrical Division: The division results in two daughter cells that are mirror images of each other, a process also known as symmetrogenic division.
- Development of Structures: In the newly formed daughter cells, structures such as the stigma, paraflagellar body, and contractile vacuole are newly developed.
Summary
Longitudinal binary fission in Euglena is a process initiated under favorable conditions, leading to the symmetrical division of the organism. Key steps include the disappearance of certain structures, division of cellular components, formation and extension of a longitudinal groove, and the development of new structures in the daughter cells. This process results in two genetically identical daughter cells, each capable of independent growth and reproduction.
SAQ-3 : What are lateral appendages? Based on their presence and absence, write the various Types of flagella giving at least one example for each type.
For Backbenchers 😎
What Are Flagella?
Flagella are like tiny tails that help some tiny creatures move around. Imagine them as tiny whip-like hairs that come out from the cell’s body.
Different Types of Flagella: Flagella can be different types based on whether they have those whip-like hairs on the sides or not. These hairs are called lateral appendages.
Atrichous Flagella: In this type, flagella are plain with no side hairs, like a simple tail. Think of it as a tail with nothing extra. An example is Escherichia coli, a type of bacteria.
Monotrichous Flagella: Here, there’s just one tail, and it might have some side hairs or not. It’s like having one whip-like tail, but it can be a bit fancy or plain. Vibrio cholerae, the bacteria that causes cholera, has this kind.
Lophotrichous Flagella: In this type, there are lots of tails all gathered at one end of the cell. Imagine having many tails all at the front. Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a bacterium with this type.
Amphitrichous Flagella: These flagella can be one or more tails at both ends of the cell. It’s like having tails at both the front and back. Alcaligenes faecalis, a type of bacteria, shows this.
Peritrichous Flagella: Peritrichous flagella are like having tails all around the cell, covering it completely. Think of a creature wrapped in tails! Salmonella typhi, which causes typhoid fever, has this type.
In Simple Words: So, flagella are like tiny tails for some tiny creatures to move around. They come in different types based on having side hairs or not. There are simple ones, fancy ones, and even ones all around the cell. These tails help creatures move and survive in different ways. It’s like nature’s way of giving them tools to get around!
మన తెలుగులో
ఫ్లాగెల్లా అంటే ఏమిటి?
ఫ్లాగెల్లా చిన్న తోకలాగా ఉంటాయి, ఇవి కొన్ని చిన్న జీవులు చుట్టూ తిరగడానికి సహాయపడతాయి. వాటిని సెల్ యొక్క శరీరం నుండి బయటకు వచ్చే చిన్న కొరడా లాంటి వెంట్రుకలుగా ఊహించుకోండి.
ఫ్లాగెల్లా యొక్క వివిధ రకాలు: ఫ్లాగెల్లా వైపులా కొరడా లాంటి వెంట్రుకలు ఉన్నాయా లేదా అనే దాని ఆధారంగా వివిధ రకాలుగా ఉండవచ్చు. ఈ వెంట్రుకలను పార్శ్వ అనుబంధాలు అంటారు.
అట్రికస్ ఫ్లాగెల్లా: ఈ రకంలో, ఫ్లాగెల్లా సాధారణ తోకలాగా పక్క వెంట్రుకలు లేకుండా సాదాగా ఉంటాయి. అదనపు ఏమీ లేని తోకగా భావించండి. ఒక ఉదాహరణ ఎస్చెరిచియా కోలి, ఒక రకమైన బ్యాక్టీరియా.
మోనోట్రికస్ ఫ్లాగెల్లా: ఇక్కడ, కేవలం ఒక తోక మాత్రమే ఉంది మరియు దానికి కొన్ని వైపు వెంట్రుకలు ఉండవచ్చు లేదా ఉండకపోవచ్చు. ఇది ఒక కొరడా లాంటి తోకను కలిగి ఉంటుంది, కానీ అది కాస్త ఫ్యాన్సీగా లేదా సాదాగా ఉంటుంది. విబ్రియో కలరా, కలరాకు కారణమయ్యే బ్యాక్టీరియా, ఈ రకమైనది.
లోఫోట్రికస్ ఫ్లాగెల్లా: ఈ రకంలో, సెల్ యొక్క ఒక చివరలో చాలా తోకలు ఉంటాయి. ముందు భాగంలో చాలా తోకలు ఉన్నాయని ఊహించుకోండి. సూడోమోనాస్ ఎరుగినోసా అనేది ఈ రకమైన బాక్టీరియం.
యాంఫిట్రిచస్ ఫ్లాగెల్లా: ఈ ఫ్లాగెల్లా సెల్ యొక్క రెండు చివర్లలో ఒకటి లేదా అంతకంటే ఎక్కువ తోకలు ఉండవచ్చు. ఇది ముందు మరియు వెనుక రెండింటిలోనూ తోకలు ఉన్నట్లుగా ఉంటుంది. ఆల్కాలిజెన్స్ ఫేకాలిస్, ఒక రకమైన బ్యాక్టీరియా దీనిని చూపుతుంది.
పెరిట్రిచస్ ఫ్లాగెల్లా: పెరిట్రికస్ ఫ్లాగెల్లా సెల్ చుట్టూ తోకలు కలిగి, దానిని పూర్తిగా కప్పి ఉంచేలా ఉంటాయి. తోకలతో చుట్టబడిన జీవి గురించి ఆలోచించండి! టైఫాయిడ్ జ్వరానికి కారణమయ్యే సాల్మొనెల్లా టైఫి ఈ రకంగా ఉంటుంది.
సాధారణ పదాలలో: కాబట్టి, ఫ్లాగెల్లా కొన్ని చిన్న జీవులు చుట్టూ తిరగడానికి చిన్న తోకలా ఉంటాయి. పక్క వెంట్రుకలు ఉన్నాయా లేదా అనే దాని ఆధారంగా అవి వివిధ రకాలుగా వస్తాయి. సెల్ చుట్టూ సాధారణమైనవి, ఫ్యాన్సీ మరియు కూడా ఉన్నాయి. ఈ తోకలు జీవులు వివిధ మార్గాల్లో కదలడానికి మరియు జీవించడానికి సహాయపడతాయి. ఇది వారికి చుట్టూ తిరగడానికి సాధనాలను ఇవ్వడం ప్రకృతి మార్గం లాంటిది!
Introduction
Lateral appendages on flagella are hair-like or whip-like projections that extend from the cell body of certain microorganisms, playing a crucial role in locomotion and sensory functions. Flagella can be categorized based on the presence or absence of these lateral appendages. This classification helps in understanding the varied mechanisms and functionalities of different types of flagella across organisms.
Types of Flagella Based on Lateral Appendages
- Atrichous Flagella:
- Description: Atrichous flagella are those that lack lateral appendages. They are smooth and unadorned.
- Example: Escherichia coli, a type of bacteria, exhibits atrichous flagella.
- Monotrichous Flagella:
- Description: Monotrichous flagella have a single flagellum with or without lateral appendages.
- Example: Vibrio cholerae, the bacterium causing cholera, has monotrichous flagella.
- Lophotrichous Flagella:
- Description: In lophotrichous flagella, multiple flagella are clustered at one end of the cell.
- Example: Pseudomonas aeruginosa is an example of a bacterium with lophotrichous flagella.
- Amphitrichous Flagella:
- Description: Amphitrichous flagella have one or more flagella at both ends of the cell.
- Example: Alcaligenes faecalis, a type of bacteria, displays amphitrichous flagella.
- Peritrichous Flagella:
- Description: Peritrichous flagella are characterized by flagella surrounding the entire cell body.
- Example: Salmonella typhi, which causes typhoid fever, has peritrichous flagella.
Summary
The presence or absence of lateral appendages on flagella leads to different types of flagella: atrichous (lacking appendages), monotrichous (single flagellum), lophotrichous (multiple flagella at one end), amphitrichous (flagella at both ends), and peritrichous (flagella surrounding the cell). Each type of flagella, exemplified by organisms like Escherichia coli, Vibrio cholerae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Alcaligenes faecalis, and Salmonella typhi, plays a vital role in the locomotion and survival of microorganisms.
SAQ-4 : Give an account of pseudopodia.
For Backbenchers 😎
What Are Pseudopodia?
Pseudopodia are fascinating, stretchy arms that some cells have. These arms are like temporary extensions, and they’re super useful for cells to get things done.
Different Types of Pseudopodia: These stretchy arms come in different shapes. For instance, some cells have thick, stubby arms called lobopodia, while others have thin, thread-like arms known as filopodia. Then there are net-like arms called reticulopodia and long, thin fingers called axopodia. Each type serves a specific purpose
How Do Pseudopodia Work?
To create these stretchy arms, cells use tiny structures inside them called actin filaments. These actin filaments help the arms stretch out when needed and bring them back in when it’s time.
What Do Pseudopodia Do?
These stretchy arms are like cell tools. They help cells do three main things. First, they help cells move around, almost like pulling themselves along. Second, they help some cells grab and eat tiny bits of food. It’s as if the cells give their food a big hug with their stretchy arms. Finally, in our bodies, certain cells use these arms to stick to surfaces and help us fight off bad things like germs.
Why Are They Important?
Scientists are really interested in pseudopodia because they help us understand how cells work. By studying them, we can figure out how cells move, how they eat, and even how they fight diseases. These stretchy arms are like the superheroes of the cell world, doing important jobs to keep things running smoothly.
In Simple Words: So, think of pseudopodia as stretchy arms for some cells. These arms help cells move, eat, and fight off bad stuff. Scientists study them to learn how cells do all these cool things. Imagine them as tiny cell superheroes with stretchy arms!
మన తెలుగులో
సూడోపోడియా అంటే ఏమిటి?
సూడోపోడియా అనేది కొన్ని కణాలను కలిగి ఉండే మనోహరమైన, సాగదీసిన చేతులు. ఈ చేతులు తాత్కాలిక పొడిగింపుల వలె ఉంటాయి మరియు వాటిని పూర్తి చేయడానికి సెల్లకు చాలా ఉపయోగకరంగా ఉంటాయి.
సూడోపోడియా యొక్క వివిధ రకాలు: ఈ సాగదీయబడిన చేతులు వివిధ ఆకారాలలో ఉంటాయి. ఉదాహరణకు, కొన్ని కణాలు లోబోపోడియా అని పిలువబడే మందపాటి, మొండి చేతులను కలిగి ఉంటాయి, మరికొన్ని సన్నని, థ్రెడ్ లాంటి చేతులను ఫిలోపోడియా అని పిలుస్తారు. అప్పుడు రెటిక్యులోపోడియా అని పిలువబడే నెట్ లాంటి చేతులు మరియు ఆక్సోపోడియా అని పిలువబడే పొడవైన, సన్నని వేళ్లు ఉన్నాయి. ప్రతి రకం ఒక నిర్దిష్ట ప్రయోజనం కోసం పనిచేస్తుంది
సూడోపోడియా ఎలా పని చేస్తుంది?
ఈ సాగే చేతులను రూపొందించడానికి, కణాలు వాటి లోపల ఆక్టిన్ ఫిలమెంట్స్ అని పిలువబడే చిన్న నిర్మాణాలను ఉపయోగిస్తాయి. ఈ యాక్టిన్ ఫిలమెంట్స్ అవసరమైనప్పుడు చేతులు చాచడానికి మరియు సమయం వచ్చినప్పుడు వాటిని తిరిగి తీసుకురావడానికి సహాయపడతాయి.
సూడోపోడియా ఏమి చేస్తుంది?
ఈ సాగే చేతులు సెల్ టూల్స్ లాంటివి. అవి కణాలకు మూడు ప్రధానమైన పనులు చేయడంలో సహాయపడతాయి. మొదట, అవి కణాల చుట్టూ తిరగడంలో సహాయపడతాయి, దాదాపుగా తమను తాము లాగడం వంటివి. రెండవది, అవి కొన్ని కణాలను చిన్న చిన్న ఆహారాన్ని పట్టుకుని తినడానికి సహాయపడతాయి. కణాలు తమ సాగిన చేతులతో తమ ఆహారాన్ని పెద్దగా కౌగిలించుకున్నట్లే. చివరగా, మన శరీరంలో, కొన్ని కణాలు ఉపరితలాలకు అతుక్కోవడానికి మరియు జెర్మ్స్ వంటి చెడు వాటితో పోరాడటానికి ఈ చేతులను ఉపయోగిస్తాయి.
అవి ఎందుకు ముఖ్యమైనవి?
శాస్త్రవేత్తలు సూడోపోడియాపై నిజంగా ఆసక్తి కలిగి ఉన్నారు, ఎందుకంటే కణాలు ఎలా పనిచేస్తాయో అర్థం చేసుకోవడానికి అవి మాకు సహాయపడతాయి. వాటిని అధ్యయనం చేయడం ద్వారా, కణాలు ఎలా కదులుతాయి, అవి ఎలా తింటాయి మరియు అవి వ్యాధులతో ఎలా పోరాడతాయో కూడా మనం గుర్తించవచ్చు. ఈ సాగదీయబడిన చేతులు కణ ప్రపంచంలోని సూపర్హీరోల వలె ఉంటాయి, పనులు సజావుగా సాగడానికి ముఖ్యమైన పనులను చేస్తాయి.
సాధారణ పదాలలో: కాబట్టి, కొన్ని కణాల కోసం సూడోపోడియాను సాగదీయగల చేతులుగా భావించండి. ఈ చేతులు కణాలను తరలించడానికి, తినడానికి మరియు చెడు విషయాలతో పోరాడటానికి సహాయపడతాయి. కణాలు ఈ అద్భుతమైన పనులన్నీ ఎలా చేస్తాయో తెలుసుకోవడానికి శాస్త్రవేత్తలు వాటిని అధ్యయనం చేస్తారు. వాటిని సాగదీసిన చేతులతో చిన్న సెల్ సూపర్హీరోలుగా ఊహించుకోండి!
Introduction
Pseudopodia, meaning “false feet,” are temporary, amoeba-like projections of the cell membrane and cytoplasm found in certain eukaryotic cells. They play a critical role in various cellular processes, including locomotion, feeding, and cellular interactions. Understanding pseudopodia is key to comprehending how certain organisms move and interact with their environment.
Characteristics and Functions of Pseudopodia
- Structure:
- Temporary Extensions: Pseudopodia are dynamic, temporary protrusions of the cell membrane and cytoplasm.
- Formation Mechanism:
- Actin Filaments: Their formation involves the assembly and disassembly of actin filaments within the cytoskeleton, allowing the pseudopodium to extend or retract.
- Types of Pseudopodia:
- Lobopodia: Thick, blunt extensions, commonly seen in Amoeba.
- Filopodia: Thin, thread-like extensions, often found in cells involved in sensing their environment.
- Reticulopodia: Net-like structures, primarily for capturing prey or attaching to surfaces.
- Axopodia: Long, thin pseudopodia supported by microtubules, used for feeding in some protozoans.
- Functions:
- Locomotion: Pseudopodia enable movement through a process called amoeboid movement, where the cell body flows into the pseudopodium.
- Feeding: In organisms like amoebae, pseudopodia are used to engulf food particles in a process known as phagocytosis.
- Cell Adhesion and Immune Response: In human cells, such as white blood cells, pseudopodia play a role in adhesion to surfaces and in the immune response.
- Significance in Research and Medicine:
- Study of Cell Motility: Pseudopodia are important in the study of cell motility and cytoskeletal dynamics.
- Cancer and Metastasis Research: Understanding pseudopodia is crucial in cancer research, particularly in studying the metastasis of cancer cells.
Summary
Pseudopodia are essential cellular structures that facilitate movement, feeding, and interaction in various eukaryotic cells. They are characterized by their dynamic and temporary nature, formed by the activity of actin filaments. Pseudopodia come in various forms, including lobopodia, filopodia, reticulopodia, and axopodia, each serving specific functions in different organisms. Their role in cell motility and immune response, as well as their significance in medical research, particularly in understanding cancer metastasis, highlights the importance of studying pseudopodia.
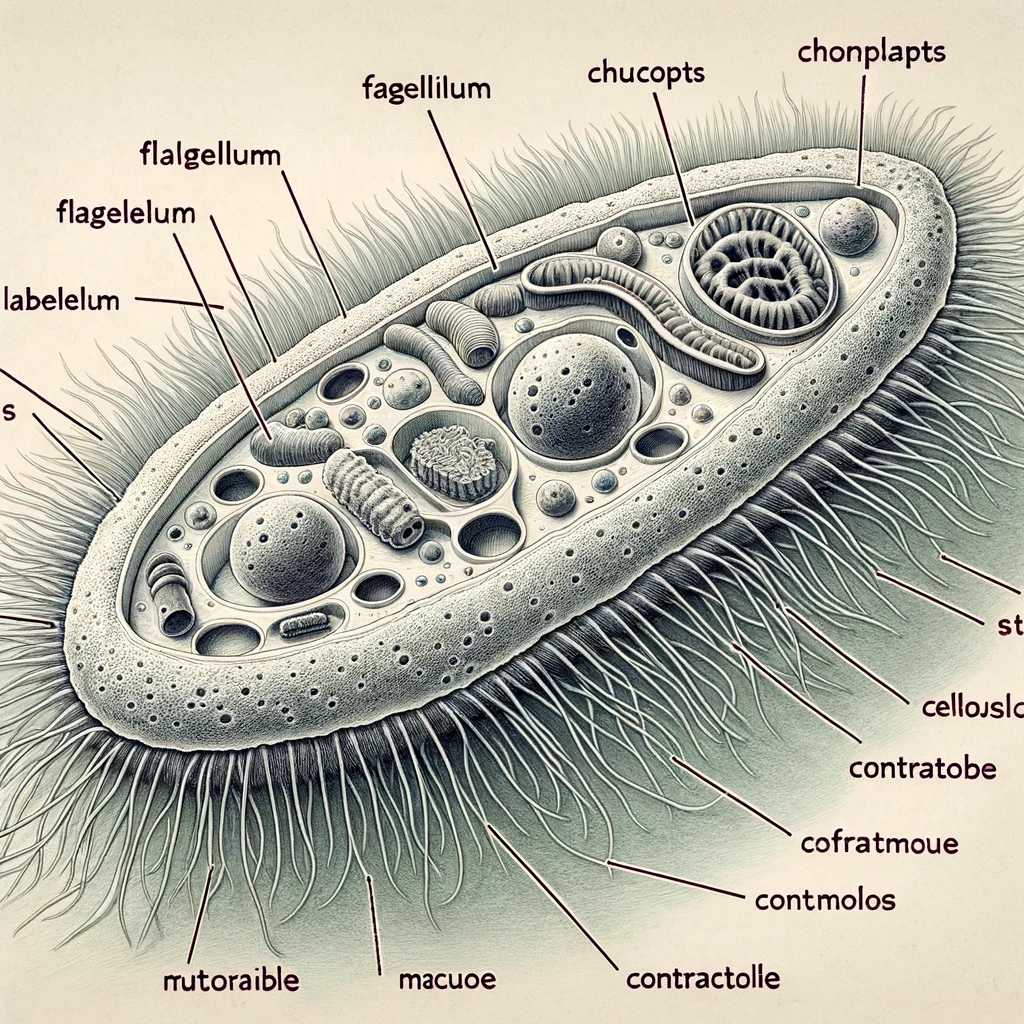
SAQ-5 : Draw a neat labelled diagram of euglena.